Groundbreaking discovery: How researchers found remnants of Earth's primordial crust near Perth
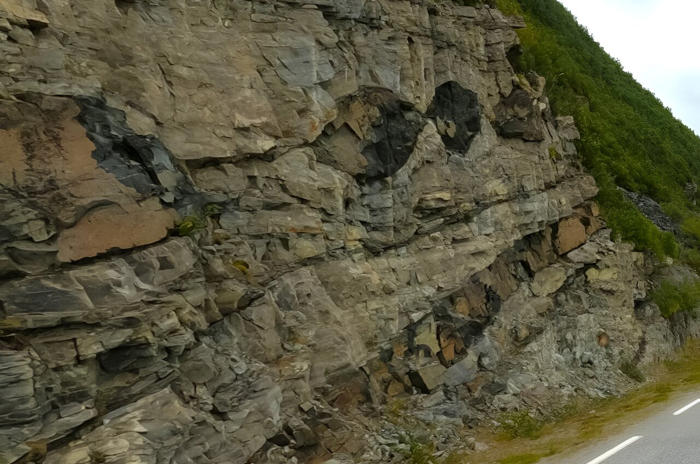

Dykes in Norway cutting into older layered sandstone rocks. Credit: Cato Andersen/Mapillary, CC BY-SA
Our planet was born around 4.5 billion years ago. To understand this mind-bendingly long history, we need to study rocks and the minerals they are made of.
The oldest rocks in Australia, which are some of the oldest on Earth, are found in the Murchison district of Western Australia, 700 kilometers north of Perth. They have been dated at almost 4 billion years old.
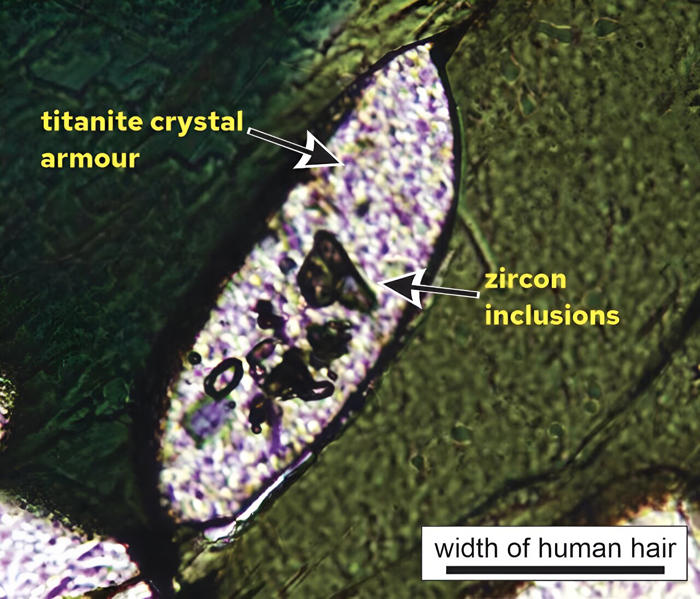
Microscope image of titanite grain with zircon crystals trapped inside and protected. The scale bar in the right bottom of image is 100 microns, about the width of a human hair. Credit: Adapted from Communications Earth & Environment (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s43247-024-01469-6
In a new study published in Communications Earth & Environment, we have found evidence of rocks of a similar age near Collie, south of Perth. This suggests the ancient rocks of Western Australia cover a far greater area than we knew, buried deep in the crust.
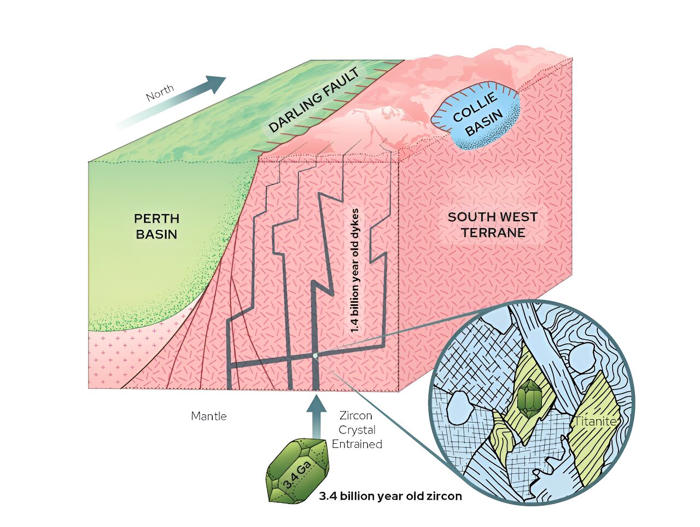
Cross-section of the crust south of Perth showing dykes picking up 3.4 billion-year-old zircon from depth and bringing it to the surface. The inset zoom-in shows the armouring of this ancient zircon by a shield of the mineral titanite. Credit: Communications Earth & Environment (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s43247-024-01469-6
The ancient continental crust
The ancient crust of Australia is crucial for understanding the early Earth, because it tells us about how the continental crust formed and evolved.
Continental crust forms the foundation of landmasses where humans live, supporting ecosystems, and providing essential resources for civilization. Without it there would be no fresh water. It is rich in mineral resources such as gold and iron, making it economically significant.
However, exploring the ancient continental crust is not easy. Most of it is deeply buried, or has been intensely modified by its environment. There are only a few exposed areas where researchers can directly observe this ancient crust.
To understand the age and composition of this hidden ancient crust, scientists often rely on indirect methods, such as studying eroded minerals preserved in overlying basins, or using remote sensing of sound waves, magnetism or gravity.
However, there may be another way to peer into the deep crust and, with luck, even sample it.
Dragging crystals up from the depths
The crust of our planet is frequently cut by dark fingers of magma, rich in iron and magnesium, which can stretch from the upper crust all the way down to Earth's mantle. These structures, known as dykes, can come from depths of at least 50 kilometers (much deeper than even the deepest borehole, which stretches a mere 12 kilometers).
These dykes can pick up tiny amounts of minerals from the depths and transport them all the way up to the surface, where we can examine them.
In our recent study, we have uncovered evidence of ancient buried rock by dating grains of zircon from one of these dykes.
Zircon contains trace amounts of uranium, which over time decays to lead. By precisely measuring the ratio of lead to uranium in zircon grains, we can tell how long ago the grain crystallized.
This method showed that the zircon crystals from the dyke date back 3.44 billion years.
Titanite armor
The zircons are encapsulated in a different mineral, called titanite, which is more chemically stable than zircon in the dyke. Think of a grain of salt, trapped inside a hard-boiled sugar sweet, dropped into a cup of hot tea.
The stability of the titanite armor protected the ancient zircon crystals through changes in the chemical, pressure and temperature conditions as the dyke traveled upward. Unshielded zircon crystals in the dyke were strongly modified during the journey, obliterating their isotopic records.
However, the grains armored in titanite survived intact to provide a rare glimpse into Earth's early history.
The dyke, itself dated to around 1.4 billion years old, has offered up a unique window into ancient crust that would otherwise have remained hidden. We also found similar ancient zircon grains further north in sand from the Swan River, which runs through Perth and drains the same region, further corroborating the age and origin of these ancient materials.
The results extend the known area of ancient crust, previously recognized in the Narryer area of the Murchison district.
One reason it's important to understand the deep crust is because we often find metals at the boundaries between blocks of this crust. Mapping these blocks can help map out zones to investigate for mining potential.
Remnants of deep time
So next time you pick up a rock and some mineral grains rub off on your hand, spare a thought for how long those grains might have been around.
To come to grips with the time scale, imagine the history of our planet was a year long. Earth formed from swirling dust 12 months ago. Any handful of sand you pick up around Perth will contain a grain or two from about ten months ago. Most of Australia's gold formed seven months ago, and land plants arrived only one month ago.
Two weeks ago, dinosaurs showed up. All of humanity has come in the past 30 minutes. And you? Soberingly, on this scale, your life would last about half a second.
More information: Christopher L. Kirkland et al, Cryptic geological histories accessed through entombed and matrix geochronometers in dykes, Communications Earth & Environment (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s43247-024-01469-6
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Provided by The Conversation
This story was originally published on Phys.org. Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest sci-tech news updates.
