New work extends the thermodynamic theory of computation
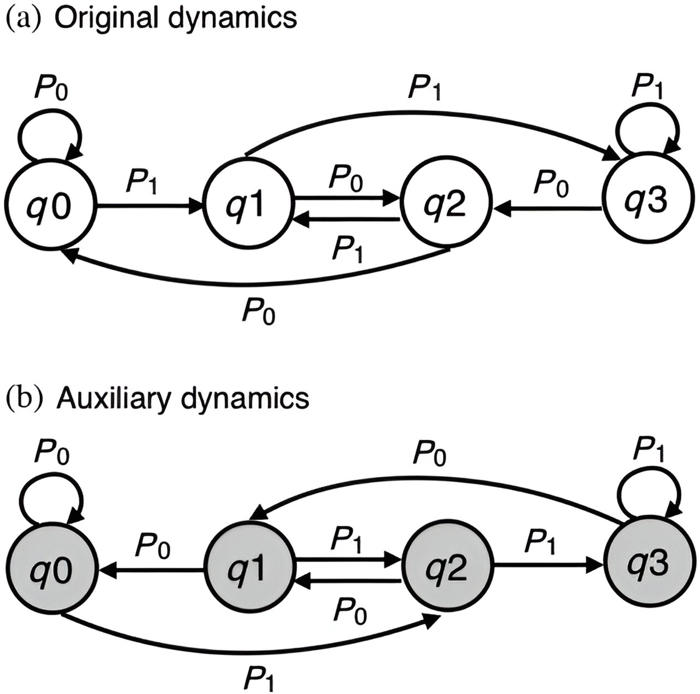
Discrete-time Markov chain (DTMC) associated with the DFA recognizing binary i.i.d. sequences that are multiple of four. The transition matrix of such DTMC is given by Eq. where p0 and p1=1−p0 denote, respectively, the probability for a 0 and a 1 in the input string. (b) DTMC associated with the auxiliary dynamics associated with the stationary prior, with transition probability matrix obtained from Eq. and given by Eq. Credit: Physical Review X (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevX.14.021026
Every computing system, biological or synthetic, from cells to brains to laptops, has a cost. This isn't the price, which is easy to discern, but an energy cost connected to the work required to run a program and the heat dissipated in the process.
Researchers at the Santa Fe Institute and elsewhere have spent decades developing a thermodynamic theory of computation, but previous work on the energy cost has focused on basic symbolic computations—like the erasure of a single bit—that aren't readily transferable to less predictable, real-world computing scenarios.
In a paper published in Physical Review X, a quartet of physicists and computer scientists expands the modern theory of the thermodynamics of computation. By combining approaches from statistical physics and computer science, the researchers introduce mathematical equations that reveal the minimum and maximum predicted energy cost of computational processes that depend on randomness, which is a powerful tool in modern computers.
In particular, the framework offers insights into how to compute energy-cost bounds on computational processes with an unpredictable finish. For example: A coin-flipping simulator may be instructed to stop flipping once it achieves 10 heads. In biology, a cell may stop producing a protein once it elicits a certain reaction from another cell. The "stopping times" of these processes, or the time required to achieve the goal for the first time, can vary from trial to trial. The new framework offers a straightforward way to calculate the lower bounds on the energy cost of those situations.
The research was conducted by SFI Professor David Wolpert, Gonzalo Manzano (Institute for Cross-Disciplinary Physics and Complex Systems, Spain), Édgar Roldán (Institute for Theoretical Physics, Italy), and SFI graduate fellow Gülce Kardes (CU Boulder). The study uncovers a way to lower-bound the energetic costs of arbitrary computational processes. For example: an algorithm that searches for a person's first or last name in a database might stop running if it finds either, but we don't know which one it found.
"Many computational machines, when viewed as dynamical systems, have this property where if you jump from one state to another you really can't go back to the original state in just one step," says Kardes.
Wolpert began investigating ways to apply ideas from nonequilibrium statistical physics to the theory of computation about a decade ago. Computers, he says, are a system out of equilibrium, and stochastic thermodynamics gives physicists a way to study nonequilibrium systems. "If you put those two together, it seemed like all kinds of fireworks would come out, in an SFI kind of spirit," he says.
In recent studies that laid the groundwork for this new paper, Wolpert and colleagues introduced the idea of a "mismatch cost," or a measure of how much the cost of a computation exceeds Landauer's bound. Proposed in 1961 by physicist Rolf Landauer, this limit defines the minimum amount of heat required to change information in a computer. Knowing the mismatch cost, Wolpert says, could inform strategies for reducing the overall energy cost of a system.
Across the Atlantic, co-authors Manzano and Roldán have been developing a tool from the mathematics of finance—the martingale theory—to address the thermodynamic behavior of small fluctuating systems at stopping times. Roldán et. al.'s "Martingales for Physicists" has helped pave the way to successful applications of such a martingale approach in thermodynamics.
Wolpert, Kardes, Roldán, and Manzano extend these tools from stochastic thermodynamics to the calculation of a mismatch cost to common computational problems in their PRX paper.
Taken together, their research point to a new avenue for finding the lowest energy needed for computation in any system, no matter how it's implemented. "It's exposing a vast new set of issues," Wolpert says.
It may also have a very practical application, in pointing to new ways to make computing more energy efficient. The National Science Foundation estimates that computers use between 5% and 9% of global generated power, but at current growth rates, that could reach 20% by 2030.
But previous work by SFI researchers suggests modern computers are grossly inefficient: Biological systems, by contrast, are about 100,000 times more energy-efficient than human-built computers. Wolpert says that one of the primary motivations for a general thermodynamic theory of computation is to find new ways to reduce the energy consumption of real-world machines.
For instance, a better understanding of how algorithms and devices use energy to do certain tasks could point to more efficient computer chip architectures. Right now, says Wolpert, there's no clear way to make physical chips that can carry out computational tasks using less energy.
"These kinds of techniques might provide a flashlight through the darkness," he says.
More information: Gonzalo Manzano et al, Thermodynamics of Computations with Absolute Irreversibility, Unidirectional Transitions, and Stochastic Computation Times, Physical Review X (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevX.14.021026
Provided by Santa Fe Institute
This story was originally published on Phys.org. Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest sci-tech news updates.
